
You’ve been looking forward to your beach getaway for months. The thought of soaking in the warm sun and swimming in the ocean sounds like heaven. But if you have sensitive skin or a condition like eczema or psoriasis, too much sun exposure can lead to irritation, rashes, and flare-ups. Choosing a sunscreen with suitable SPF and ingredients is critical to protecting your skin without causing a reaction.
If you have sensitive skin, eczema, or psoriasis, choosing the correct SPF is critical for avoiding irritation and flare-ups. The higher the SPF, the more protection you’ll get from UVB rays that cause sunburns, but SPF only indicates protection from UVB, not UVA which penetrates deeper and causes ageing and skin damage.
These tips will help protect you from the sun without aggravating your sensitive skin or conditions. The key is using a high-quality, mineral-based sunscreen free of potential irritants, reapplying regularly, and limiting sun exposure when possible. Your skin will thank you, and you can enjoy your outdoor adventures confidently.
When it comes to sun protection for sensitive skin, the type of sunscreen you choose matters. Mineral sunscreens, also called physical blockers, contain zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide to block UV rays physically. Chemical sunscreens absorb UV radiation to protect your skin. For sensitive skin, mineral sunscreens are typically gentler and less irritating.
Mineral sunscreens sit on top of the skin to deflect the sun’s rays. They are less likely to cause a reaction or irritation because the ingredients remain on the skin’s surface. Chemical sunscreens, on the other hand, are absorbed into the skin and may trigger a sensitivity or allergic reaction in some people.
They often contain compounds like oxybenzone, octinoxate, and avobenzone, which can be irritating.
When shopping for sunscreen, check the active ingredients. Look for mineral sunscreens with zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide, natural mineral compounds. Avoid sunscreens with harsh chemicals like oxybenzone or octinoxate. Mineral sunscreens labelled non-nano or uncoated are best since the particles are too large to be absorbed into the skin.
For the most sensitive skin, choose a mineral sunscreen that is fragrance-free, paraben-free, and specifically designed for sensitive skin. Do a patch test on your inner arm before applying it all over. With the right mineral sunscreen and some common sense sun protection tips, you can enjoy your outdoor adventures without worrying about a sun sensitivity flare-up.
The best sunscreens for sensitive skin contain mineral ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide. These provide broad-spectrum protection from UVA and UVB rays without irritating the skin.
In summary, mineral sunscreens are the most gentle and effective for sensitive skin and conditions like eczema or psoriasis. Look for those with high concentrations of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, and avoid potential irritants like fragrances, parabens and chemical UV filters. Using mineral sunscreen and other sun protection methods like wearing hats and limiting sun exposure during the peak UV hours of 10 AM to 4 PM can help prevent sunburns and skin damage for those with sensitive skin.
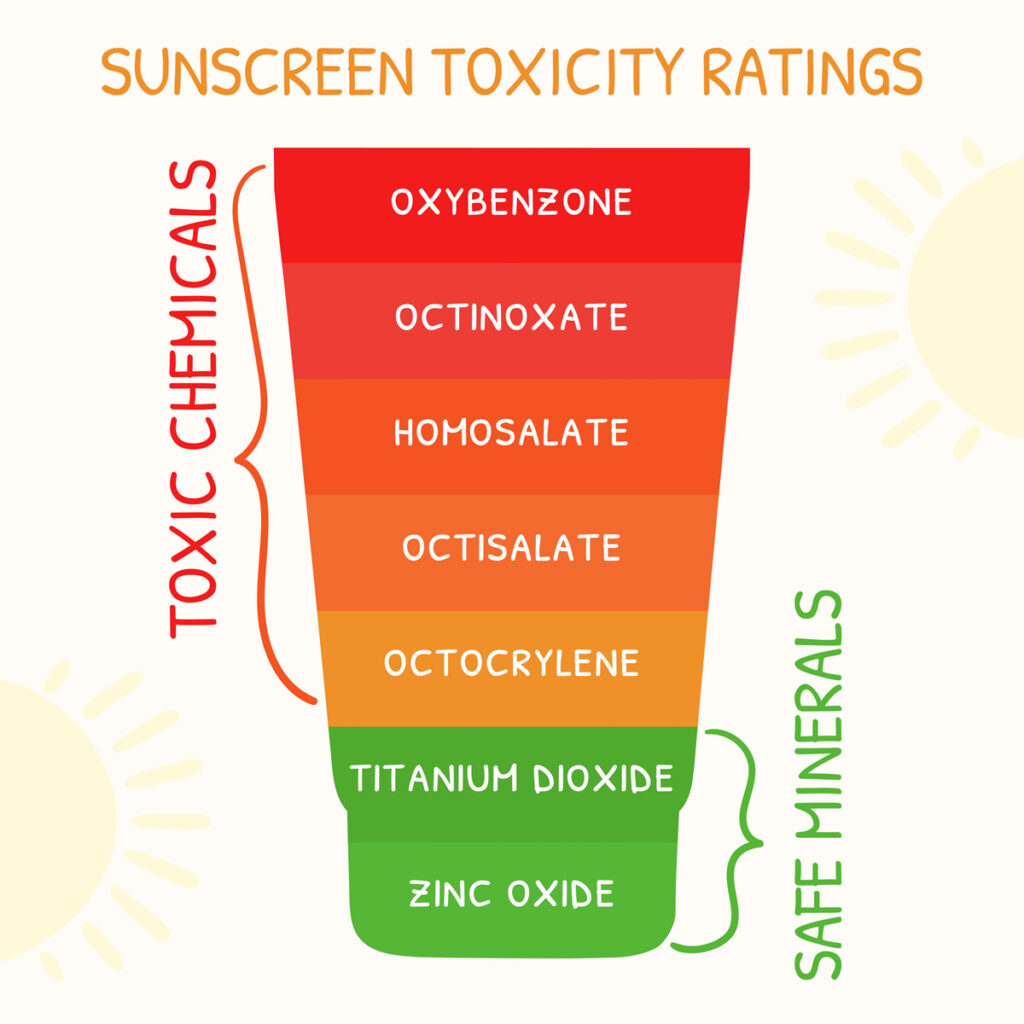
When choosing a sunscreen for sensitive skin, look for specific ingredients that can irritate or inflame. Avoiding these potential irritants is vital to finding a gentle, soothing sun protection product.
Artificial fragrances are common irritants for sensitive skin. Even natural essential oils can be irritating for some. To ensure the fragrance used is natural and low in percentage, It’s best to avoid fragrances altogether if in doubt.
Parabens are preservatives used in many cosmetics, including sunscreens. They can be irritating and may be linked to hormone disruption. Check the ingredients list and avoid products containing parabens like methylparaben, propylparaben, and butylparaben.
Oxybenzone is a chemical sunscreen agent that can cause allergic reactions and harm the environment. Mineral-based sunscreens with zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are gentler alternatives. They sit on top of the skin to physically block the sun rather than being absorbed into the skin.
Isopropyl alcohol is added to some sunscreens as a solvent but can dry out and irritate sensitive skin. An alcohol-free sunscreen is best, especially if you have eczema or psoriasis.
Preservatives like DMDM hydantoin and imidazolidinyl urea release formaldehyde, a known skin irritant. They are common in water-based products like sunscreens. Check the ingredients and avoid these formaldehyde releasers.
By avoiding fragrances, parabens, oxybenzone, alcohol, and formaldehyde in your sun protection products, you’ll be well on your way to finding a gentle, non-irritating sunscreen for your sensitive skin. And when in doubt, do a patch test on your inner arm before slathering it all over; your skin will thank you!
Find out More About What to Avoid
When you have sensitive skin, eczema or psoriasis, finding a sunscreen that doesn’t irritate your skin can be tricky. A no-sting sunscreen is specially formulated for sensitive skin and conditions like eczema. It should be free from common irritants in regular sunscreens that can sting or burn sensitive skin.
When choosing a no-sting sunscreen, consider the following:

Using a no-sting, broad-spectrum sunscreen formulated for sensitive skin, along with other sun protection methods like wearing hats and limiting sun exposure during the peak UV hours of 10 AM to 4 PM, can help prevent sunburn and allow you to enjoy outdoor activities without discomfort. Be sure to reapply sunscreen every 2 hours or after swimming or sweating heavily for the best protection.
So there you have it, the lowdown on choosing the right sun protection for your sensitive skin. The most important things to remember are to look for mineral-based sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, avoid harsh chemicals like oxybenzone or octinoxate, and choose a broad-spectrum UVA/UVB cream.
Test any new sunscreen on a small skin patch first to ensure it doesn’t irritate you. And don’t forget, the best way to prevent sun damage is limiting sun exposure, wearing UV-protective clothing, and reapplying sunscreen every 2 hours. Your skin will thank you for taking these extra precautions. Now get outside and enjoy your adventure – safely!
What is SPF, and why is it important for sensitive skin?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor, which measures sunscreen protection against UVB rays. For individuals with sensitive skin, it is crucial to use sunscreens with a high SPF to prevent sunburn and potential skin damage. SPF shields the skin by blocking harmful UV rays that can trigger reactions or exacerbate existing skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
What does “no sting” mean in relation to sun creams for sensitive skin?
“No sting” refers to sun creams specifically formulated to minimize stinging or discomfort when applied to sensitive or damaged skin. These products are designed to be gentle and less irritating, ensuring a more comfortable experience while providing sun protection.
How does SPF sun cream affect eczema and psoriasis?
SPF sun creams help protect the skin affected by eczema and psoriasis from sunburn and potential aggravation. Sun exposure can trigger flare-ups and worsen symptoms in individuals with these conditions. By using SPF sun creams regularly, you can help create a barrier between your skin and harmful UV rays, reducing the likelihood of irritation and supporting the management of eczema and psoriasis.
What are some natural ingredients suitable for sensitive skin in SPF sun creams?
Natural ingredients can offer gentle yet effective protection for sensitive skin. Some suitable options include:
– Zinc oxide: A mineral ingredient that provides broad-spectrum protection while being gentle on the skin.
– Titanium dioxide: Another mineral ingredient that reflects UV rays without irritating.
– Cocoa butter: Known for its soothing properties, it can help calm and hydrate sensitive skin.
– Almond oil: Rich in antioxidants, almond oil can offer additional protection against free radicals and help reduce inflammation.
Can sun creams with natural ingredients effectively protect against UV rays?
Yes, sun creams with natural ingredients can provide effective protection against UV rays. Look for products labelled as broad-spectrum, indicating they protect against UVA and UVB rays. Natural ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide act as physical blockers, reflecting and scattering UV rays away from the skin.
How frequently should I apply SPF sun cream to sensitive skin?
It is generally recommended to reapply SPF sun cream every two hours or more frequently if swimming or sweating. This regular application ensures consistent protection, especially for individuals with sensitive skin who may be more susceptible to sunburn or irritation.
Can SPF sun creams worsen skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis?
SPF sun creams specifically formulated for sensitive skin are generally designed to minimize the risk of aggravating existing skin conditions. However, individual reactions may vary. It is advisable to patch-test new products and consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional if you have concerns about specific ingredients or potential reactions.
Are there any additional measures to protect sensitive skin from the sun?
Along with using SPF sun creams, consider other sun protection measures, such as seeking shade.
Wear protective clothing (e.g., wide-brimmed hats, long sleeves), and use sunglasses to shield your eyes from harmful UV rays. These precautions can complement sun creams and further protect sensitive skin.
Can I use SPF sun creams on children with sensitive skin?
SPF sun creams formulated for sensitive skin are generally safe for children. However, choosing products specifically designed for children is essential and consult with a doctor or dermatologist if you have any concerns. Additionally, for infants under six months old, avoiding direct sun exposure and seeking alternative forms of sun protection, such as shade and protective clothing, is advisable.